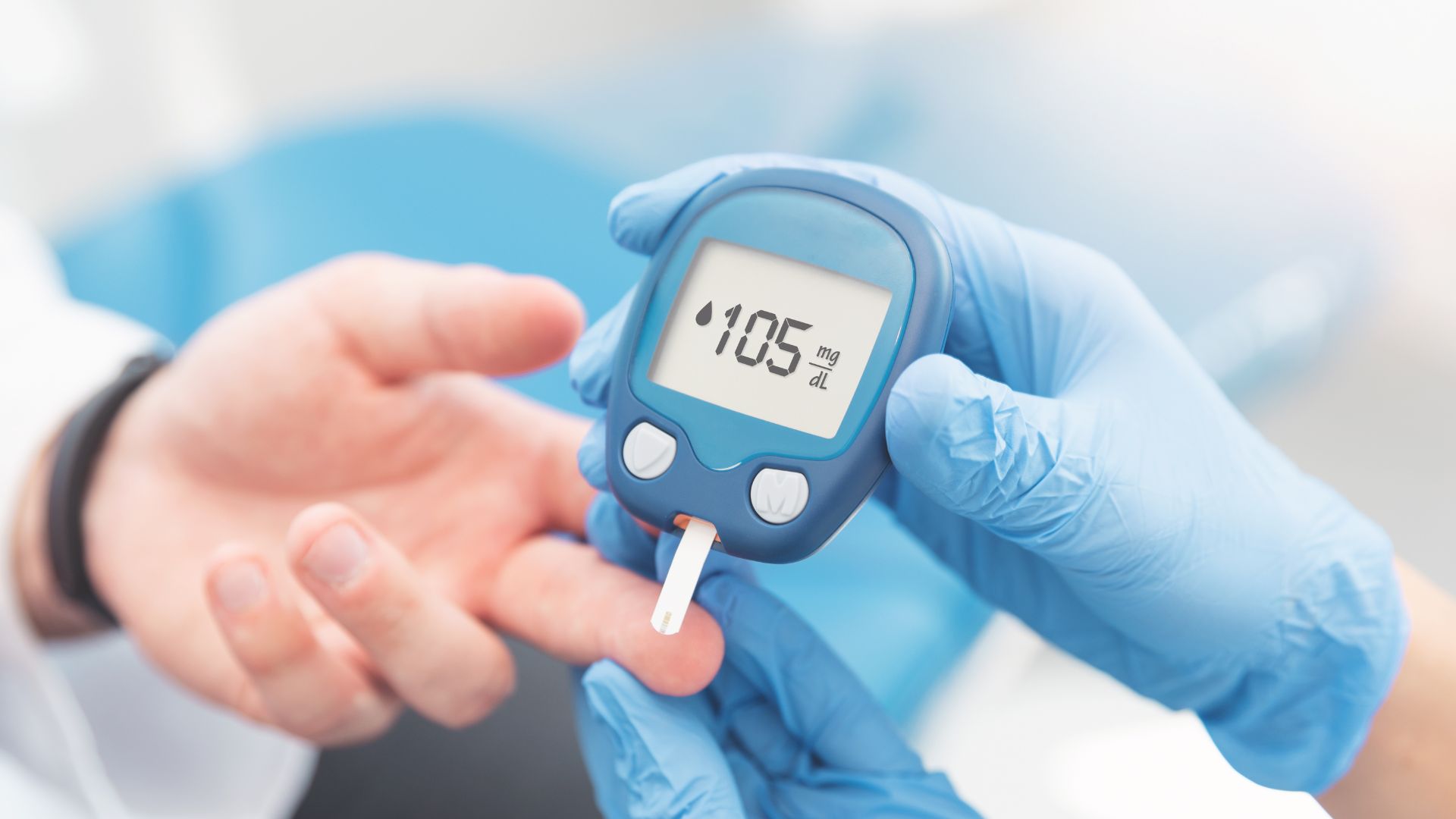
Diabetes mellitus, also known as diabetes, is a metabolic disease that causes high blood sugar levels. Diabetes develops when our body cannot absorb sugar (glucose) and use it for energy. This causes an accumulation of extra sugar in our bloodstream. Diabetes comes in many forms, each with its own set of causes, but they all share the problem of having too much glucose in your bloodstream. Medication and/or insulin are used as treatments. A healthy lifestyle can help prevent some types of diabetes. You may visit primary care physician Sugar Land, Lifetime Primary Care to make an appointment with Dr. Misbah Kalair, MD is a Family Medicine Specialist in 16645 W Airport Blvd, Sugar Land, TX- 77498.
Symptoms
Our blood sugar level determines our diabetes symptoms. Some people, especially those with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes, may not have any symptoms. Type 1 diabetes symptoms appear quickly and are more severe.
Symptoms of type 1 and type 2 diabetes include:
- Having more thirst than usual.
- Frequent urination
- Losing weight without putting forth any effort.
- Urine ketone levels.
- Being tired and weak.
- Being irritable or having other mood swings.
- Having blurry vision.
- Having slow-healing sores.
- Recurrent infections, such as gum, skin, and genital infections.
Types of Diabetes
Diabetes is classified into three types: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is thought to be an autoimmune disorder. This means that the immune system attacks and destroys the beta cells in our pancreas that make insulin by mistake. Type 1 diabetes affects approximately 5-10% of all diabetics. Type 1 diabetes symptoms frequently appear fast.
Type 2 diabetes
Insulin resistance is the first sign of type 2 diabetes. This means that our bodies cannot use insulin efficiently, causing our pancreas to produce more insulin until it can no longer meet demand. Insulin production then declines, resulting in high blood sugar. Type 2 diabetes affects 90-95% of diabetics.
Gestational Diabetes
Pregnant women who have never had diabetes develop gestational diabetes. If anyone has gestational diabetes, their baby may be more vulnerable to health problems. Gestational diabetes usually disappears after the baby is born.
The common complication of diabetes
High blood sugar levels harm organs and tissues throughout the body. The higher the blood sugar level is and the longer we live with it, the more likely we are to develop complications.
Diabetes complications include the following:
- Stroke, heart attack, and heart disease
- Neuropathy
- Nephropathy
- Retinopathy and vision impairment
- Loss of hearing
- Infections and sores that do not heal on the feet, skin conditions such as bacterial and fungal infections
- Depression
Consultation with Diabetes Doctor:
A patient should see a diabetes doctor in the following situations:
- Initial diagnosis or presence of diabetes symptoms.
- Difficulty managing blood sugar levels.
- Diabetes-related complications.
- Type 1 diabetes, which requires specialized care.
- Gestational diabetes during pregnancy.
- Suboptimal response to treatment or frequent episodes of high or low blood sugar.
- Considering insulin pump or continuous glucose monitoring.
- Regular check-ups for ongoing care, even when diabetes is well-managed.
Consulting a diabetes doctor is crucial for maintaining optimal health and preventing complications related to diabetes. Visit CDC website for more relevant information.
A Diabetes Doctor
A diabetes doctor, also known as an endocrinologist, is a medical specialist who focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of hormone-related disorders, including diabetes. Endocrinologists have extensive knowledge of the endocrine system, which produces and regulates hormones in the body.
In the case of diabetes, endocrinologists specialize in managing both type 1 and type 2 diabetes and other less common forms of the disease. They work closely with patients to develop personalized treatment plans to control blood sugar levels, prevent complications, and improve overall health.
Some of the key responsibilities of a diabetes doctor include:
-
Diagnosing diabetes: Endocrinologists use various diagnostic tests, such as blood glucose tests and hemoglobin A1c tests, to determine if a patient has diabetes and to classify the type of diabetes they have.
-
Managing blood sugar levels: They create individualized treatment plans, which may involve prescribing insulin or oral medications, to help patients maintain optimal blood sugar levels.
-
Monitoring complications: Diabetes doctors regularly monitor patients for potential diabetes-related complications, such as kidney damage, nerve damage, eye problems, and heart disease, to ensure early detection and treatment.
-
Lifestyle counseling: Endocrinologists provide guidance on making healthy lifestyle choices, such as maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress, to help patients better manage their diabetes.
-
Patient education: They educate patients about the importance of self-monitoring blood sugar levels, recognizing the signs of high or low blood sugar, and understanding how different factors (e.g., food, exercise, stress) can affect blood sugar levels.
-
Coordinating care: Diabetes doctors often collaborate with other healthcare professionals, such as primary care physicians, dietitians, and podiatrists, to provide comprehensive patient care.
If you have diabetes or suspect you might have it, it’s essential to see a diabetes doctor (endocrinologist) to receive proper diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing care. Regular visits with an endocrinologist can help you effectively manage your diabetes and maintain good overall health. Visit Lifetime Primary Care Sugar Land to make an appointment with Dr. Misbah Kalair, MD, a Family Medicine Specialist for diabetes care. The clinic is convenient located at 16645 W Airport Blvd, Sugar Land, TX- 77498.